November 28, 2024 | 07:16 pm
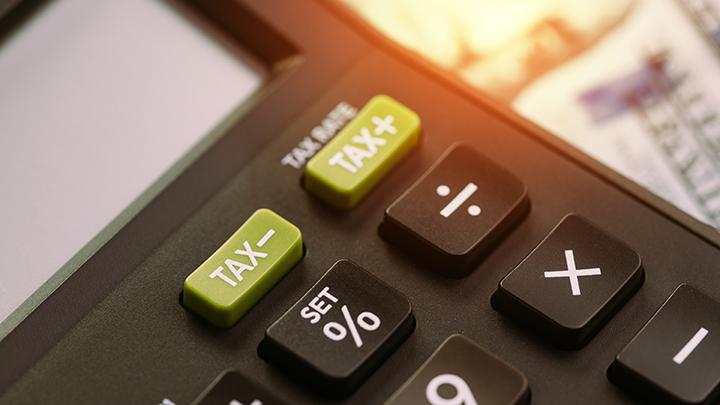

TEMPO.CO, Jakarta - Some countries around the world rely on taxation as their primary source of revenue. Take the United Kingdom (U.K.) as an example. According to IFS TaxLAB, the government collects approximately £1 trillion annually from three of its largest taxes: income tax, NICs, and VAT.
Speaking of VAT, the term stands for Value-Added Tax. It simply refers to the tax added to products and services. Many apply VAT because it has the potential to raise resources and modernize the overall tax system, according to a recent study by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
In this article, we'll help you understand the basics of VAT and how it works, citing Investopedia, the IMF, and other sources. So, what is a VAT? Scroll down to learn more.
What is a Value-Added Tax (VAT)?
A VAT refers to a consumption tax imposed on goods and services at each stage of the supply chain, from production to distribution. This tax is passed on to the end-user, which is the customer and is equally charged on every purchase.
The official website of gov.uk specifies that things levied with the VAT may include
- goods and services;
- hiring or loaning goods to someone;
- selling business assets;
- commission; and others.
According to Investopedia, the creation of the VAT was largely in the hands of Europeans. Although some believe that the idea of taxing each stage of production originated in Germany, others credit Maurice Lauré, a French tax official, who came up with the idea of VAT in 1954.
The tax system soon became prominent. According to the OECD, as of January 2014, more than 160 countries in various regions, including Europe, Africa, Asia and Oceania, have implemented VAT. This tax is particularly important for European Union (EU) member countries, as it serves as a crucial resource for their budgets.
Despite its popularity, some countries, such as Bermuda, the Cayman Islands, and Qatar, have chosen to operate without VAT. This is largely because they have a more robust revenue stream than taxation, such as tourism and oil extraction.
How VAT Works
In most cases, the mechanism of VAT can be similar in any country that adopts the system. According to the official website of the Dutch government, since VAT is levied on the price of goods and services, it's the customer who pays the tax to the merchant. The trader then remits the VAT to the Tax and Customs Administration.
The same mechanism is used in Indonesia. According to djpb.kemenkeu.go.id, VAT-registered merchants are responsible for collecting VAT from the consumers of the invoiced products or services at 10 percent of the selling price or replacement value.
Later, these traders should issue a tax invoice as proof of collection and submit the VAT Periodic Notification Letter to the relevant tax office on a monthly basis.
To better understand how VAT works, here's a simple example taken from the official website of the Dutch government:
A trader wants to sell a bicycle. He first calculates the selling price of the bicycle without VAT. He then multiplies the selling price by the VAT rate to calculate the amount of VAT to charge. He adds this to his selling price, giving the price the buyer actually pays. After the bicycle is sold, the trader remits the VAT to the Tax and Customs Administration.
Pros and Cons of VAT
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of VAT implementation as highlighted in Investopedia:
Pros
- VAT serves as a smart alternative to provide governments with more consistent revenue.
- VAT helps minimize tax loopholes since it is collected at multiple levels.
- VAT provides a stronger incentive to earn, as well as encourages savings, and discourages frivolous spending.
Cons
- Implementing a VAT may lead to an increase in the price of products and services.
- Businesses may face challenges in complying with VAT regulations, resulting in additional costs.
- Additional taxes on goods and services may lead to tax evasion.
As mentioned earlier, some countries don't rely on taxation as a source of revenue. Find your way to our previous list of countries with no income tax to gain more insights.
Investopedia | OECD
Editor's Choice: Luhut Reveals Why Prabowo Delay the 12% VAT Implementation in Indonesia
Click here to get the latest news updates from Tempo on Google News
Cryptocurrency Taxes: How They Work and What You Need to Know
2 jam lalu

In response to the growing virtual currency market, the IRS shares comprehensive guidelines on cryptocurrency taxes. Read on to learn more.
Apindo Protests Ever-changing Minimum Wage Formula: 'Business Players Need Certainty'
5 jam lalu

Indonesian Entrepreneurs Association (Apindo) argues that the continually changing provincial minimum wage formula has negative impact on businesses.
Luhut Reveals Why Prabowo Delay the 12% VAT Implementation in Indonesia
8 jam lalu

Pros and cons of adopting 12% VAT by January 1, 2025 were addressed by Economic Council Chair Luhut, who claimed that Prabowo would postpone it.
Indonesia's 12% VAT Uproar, Here Are 6 Characteristics of Middle Class in the Country
1 hari lalu

Indonesia's middle class group includes people with expenditure ranging from Rp2,040,262 to Rp9,909,844 per capita per month in 2024.
Economic Council Chair Luhut Says 12% VAT to Be Postponed
1 hari lalu

Chair of the National Economic Council Luhut responded to the public outcry over the planned implementation of a 12% Value Added Tax (VAT) in 2025.
Indonesian Govt Criticized for Lack of Transparency on 12 Percent VAT
3 hari lalu

The Central Information Commission (KIP) assesses that the Indonesian government is not transparent in conveying socialization of the 12 Percent VAT.
VAT Hike to Drive Up Textile Prices by 21.6%, Says Association
3 hari lalu
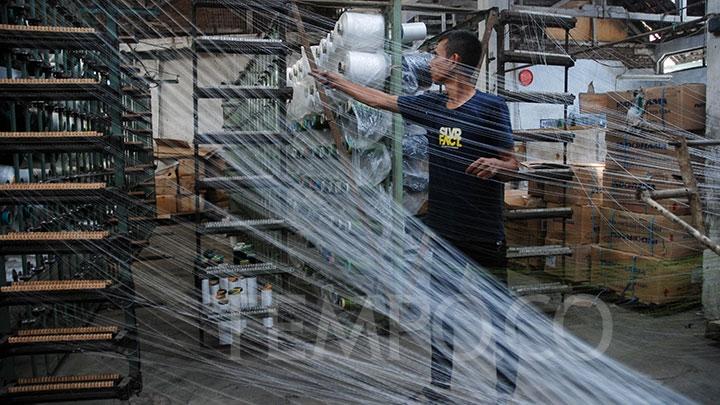

Textile entrepreneurs warned that the additional costs incurred by producers due to the VAT hike to 12% will be passed on to consumers.
House Prices Expected to Rise Due to 12 Percent VAT Effect
3 hari lalu

House prices are expected to increase in line with the increase in value-added tax or VAT to 12 percent starting January 2025.
Today's Top 3 News: 10 Cheapest Currencies in the World 2024, Indonesia is on the List
3 hari lalu

Tempo English compiled the top 3 news on Sunday, November 24, 2024.
Economists Say 12% VAT Implementation Will Burden Indonesian Middle Class Even More
4 hari lalu

Several economists consider that the implementation of 12% of Value Added Tax (VAT) will further burden the middle class in Indonesia even more.

 3 months ago
80
3 months ago
80













































